Boost Your Trading Skills with the RSI Divergence Strategy


In 1987, J. Welles Wilder Jr.–an American mechanical engineer who became famous for his enormous contributions to technical analysis–introduced the Relative Index Strength indicator, also known as RSI.
The RSI is a momentum oscillator indicator that measures the speed and magnitude of price movements. It provides insights into whether a currency or asset is oversold or overbought, allowing you to buy or sell when markets irrationally take prices too low or too high.
Besides being used for several techniques, many traders use the RSI indicator to identify divergences and forecast potential reversals. RSI divergence happens when the movement in the indicator contradicts the movements you see in the price chart.
In this article, we will explore the concept of RSI divergence and walk through a step-by-step guide for detecting, interpreting, and making trading decisions effectively while using this technique.
The RSI is one of the best momentum indicators to measure the pace and intensity of the most recent changes in the price of an asset. Its values range from 0 to 100, helping you assess whether an asset is overbought (over 70) or oversold (below 30). This technical indicator reacts to price changes by comparing the average gains and losses over a specific time window, usually 14 periods, and usually moves alongside price (i.e., when prices go up, the RSI goes up).
Whenever there is a deviation in the correlation between price and indicator–prices going up while RSI goes down–we are potentially dealing with an RSI divergence.
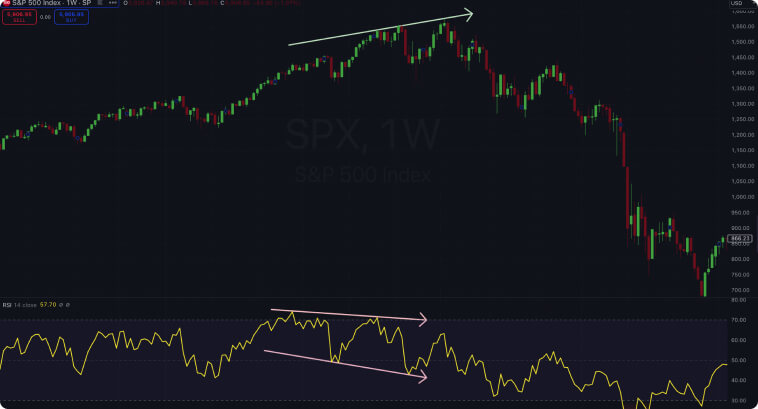
The image below provides a textbook example of divergence. Bitcoin prices appear to be in an uptrend, while the RSI indicator is trending downwards.
If an asset consistently makes higher highs while the RSI makes a lower low, it may point to a weakening uptrend. This divergence suggests that bears could gain momentum at any point, driving prices lower.
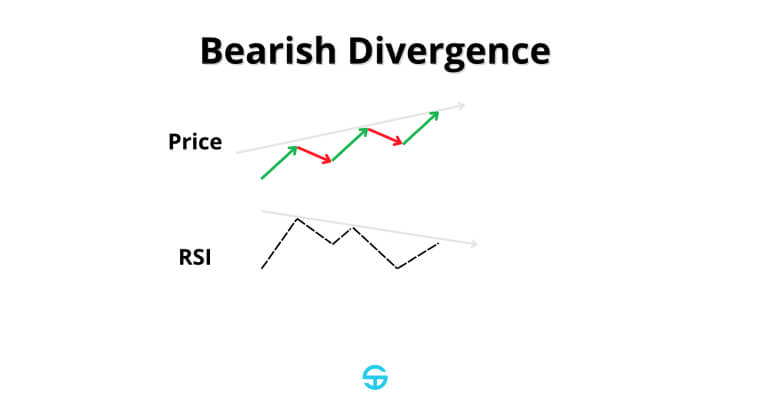
RSI divergences can fall into two main categories: Bullish and Bearish RSI divergence.
Bullish divergences occur when the price makes a lower low, but the RSI forms a higher lower.
This type of movement indicates that selling pressure is weakening, so the buy-side might gain enough strength to push prices higher and put an end to the downtrend.
It is more reliable when found at the bottom of a downtrend and aligned with oversold RSI levels.
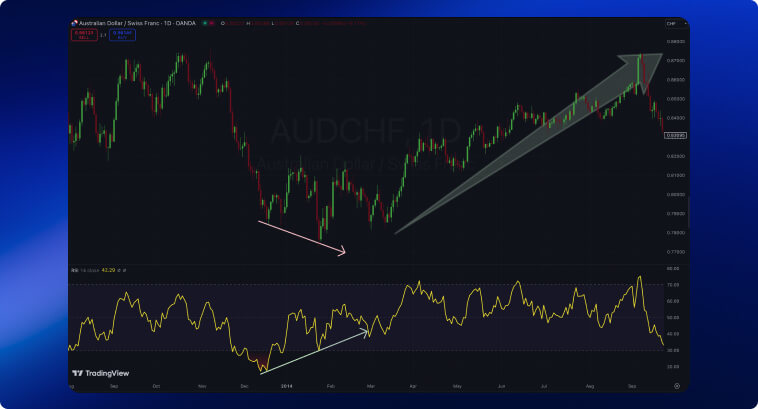
Bearish divergences, on the other hand, are marked by prices reaching a new high with lower highs on the RSI.
This divergence also points towards weakening strength among bulls, which empowers bears to take prices to lower levels and kickstart a downtrend.
This pattern is also more reliable when found at the peak of an uptrend and aligned with overbought RSI levels.
Spotting divergences on a price chart might not always be that straightforward. Not all divergences are relevant, either.
You can follow a similar approach to the one outlined below to enhance your chances of success when developing divergence-based trading strategies.
• Identify a downtrend where bears/sellers have consistently pushed prices lower
• Pinpoint the lows in price and compare them with the lows on the RSI chart
• A bullish divergence occurs when prices form a lower low, but RSI forms a higher low.
• Attention: If divergence forms when RSI is at oversold levels–below 30–that can indicate that bulls/buyers might be at a key moment to seize control over the price.

• Identify an uptrend where prices are consistently going up, forming higher highs and higher lows.
• Compare the price chart’s peaks with the peaks of the RSI values.
• If prices are reaching higher highs but the RSI forms a lower high, that is a sign of exhaustion of the uptrend.
• Attention: It is preferable that the divergence forms when RSI is under overbought conditions.
The RSI indicator is available on most trading software nowadays. My number one choice is TradingView, where you can pick from a wide selection of built-in indicators, along with others developed by the trading community–you can see our blog post on the best TradingView indicators for day trading to explore a bit more on this topic.
On TradingView, you can simply look for “RSI” on the Indicators menu to find the built-in Relative Strength Index, which is very well done. You can change the colors of the RSI, use a moving average alongside it, and tweak it in any way you would like.
The main parameters to have in mind when adjusting the RSI to your liking are:
When used correctly, divergence trading can be extremely effective in getting in early on a trend reversal.
Considering that bullish divergences indicate an upward reversal, they offer you the opportunity to profit by going long when price action confirms that the buy-side took control over the trend and will drive the price to higher levels. Bullish divergences are spotted when the RSI forms higher lows while the price forms lower lows, pointing to diminishing selling pressure. The reversal can be confirmed via candlestick patterns like the bullish engulfing or hammer, serving as entry points.
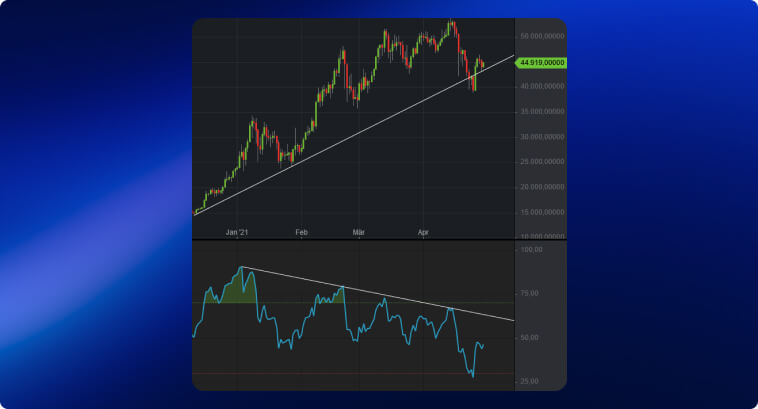
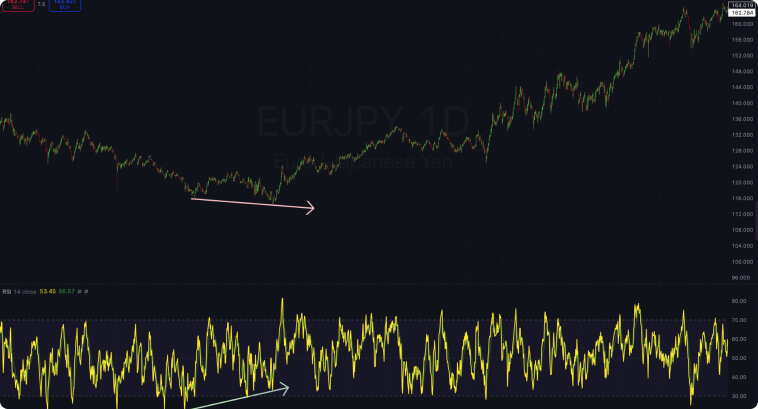
The image below depicts an example of bullish divergence on the EURJPY currency pair. The pattern tends to be more reliable when it appears after a consistent decline in prices and when the RSI achieves an oversold level.
Bearish divergences, on the other hand, are designed to spot downward reversals. In this case, we are going short as soon as we have a confirmation that the sell-side took control over the price. We will look for a pattern where the price forms higher highs, but the RSI forms lower highs. Confirmation happens when a bearish candlestick pattern like the shooting star or bearish engulfing appears.
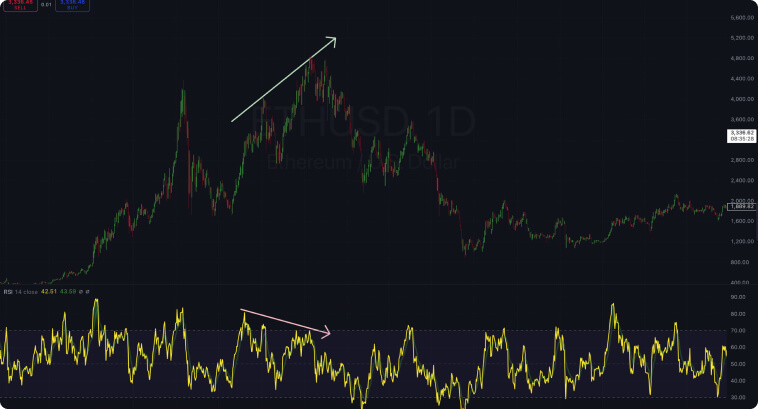
The example below shows a bearish divergence on the daily chart for Ethereum. Prices are in an uptrend until the RSI forms lower highs, indicating that bulls are losing their strength over the trend, taking prices down right after.
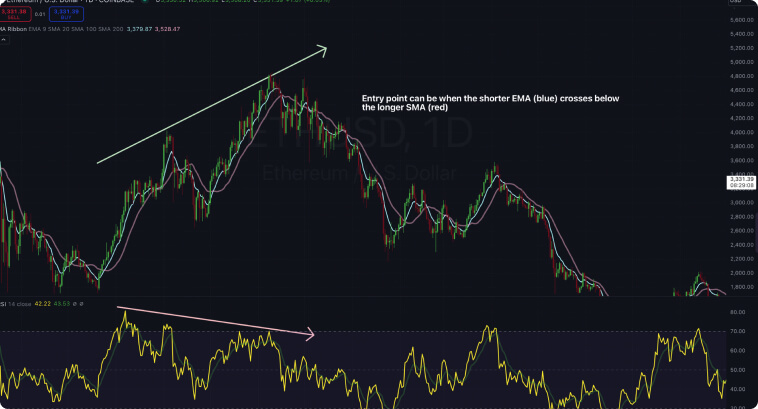
Divergence-based trading systems can become more accurate when combined with other technical techniques. Moving averages, for example, can help you define entry points (entry when a shorter moving average crosses up or down the longer moving average, depending on whether you’re looking at a bullish or bearish divergence)
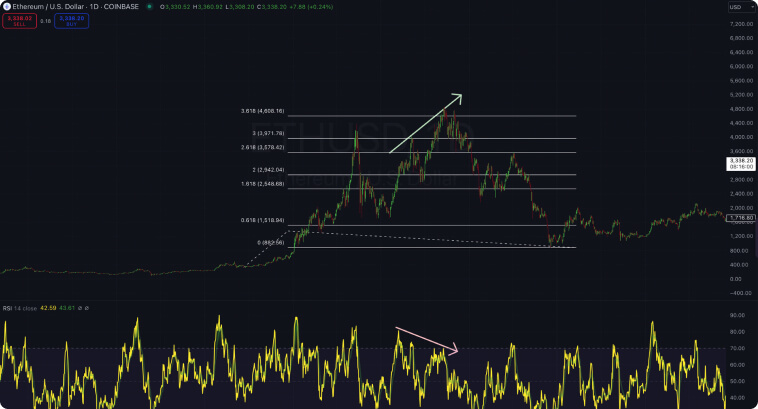
Fibonacci extensions or retracements can also help you identify relevant key points of support or resistance to help improve the analysis. For example, a divergence around relevant levels (e.g., 3.618) provides a good chance that the current trend has reached exhaustion, and the counterparty may have enough strength to push prices toward their direction.
Even though trading systems based on RSI divergences are powerful, they also tend to display false and unreliable signals. False divergences tend to occur in sideways markets or during periods of lower trading volume. Knowing how to filter out false signals is crucial to avoid entering trades way too early or in the wrong direction, which is why you can use the check-list below to help you asses when a divergence is truly relevant:
Risk management is the most important component of any trading system. Limit each trade to 1-2% of your total trading account and calculate position size based on stop-loss distance. Stop-loss should be set either below the lowest low for bullish divergences or above the highest high for bearish ones, for example. Profit targets can be around support and resistance levels, Fibonacci extension or retracement levels, or on a minimum risk-reward ratio such as 1:2.
Unfortunately, false signals are a common challenge. Avoid entering trades when the market is in consolidation, where no trend is apparent (you can use moving averages to help you identify that). Avoid any trade when volume is below average, as that indicates low interest from market participants, causing the prices to make erratic movements.
Typical mistakes come from misreading the RSI signals or relying solely on this indicator for confirmation. Not all divergences lead to reversals, so the broader context of the market should be taken into consideration before any entries. Trading volume, Fibonacci levels, support and resistance levels, and Bollinger Bands are your allies in identifying when a reversal is about to happen. Stay away from range-bound markets when trading divergence-based strategies.
RSI divergences are highly popular due to their effectiveness in identifying trend reversals, providing early signals of market shifts, and allowing you to ride the trend right from the start. Moving averages, Fibonacci retracements and extensions, plus volume analysis can help you improve reliability and maximize gains when developing a divergence-based trading system. For this particular strategy, focus on trending markets and combine trading signals with overbought and oversold RSI levels for better results.
Before risking your money, consider practicing on demo accounts to refine your skills and pair them up with a strong risk management plan. Use stop-loss and profit targets to maintain discipline and validate signals with the extra context of the market. The RSI divergence strategy can be a highly valuable component of any trading system when applied correctly.
While the RSI is widely applied in chart-based trading systems, several investors tend to consider the “bigger picture” before entering a position. To better understand how chart-based trading systems relate to and contrast with fundamental approaches, take a look at our article on technical vs fundamental analysis, as both can highly enhance your trading system and success.